ILRI’s Jimmy Smith (left) and the World Bank’s Francois Le Gall are co-hosting a high-level consultation for a global livestock agenda to 2020 at ILRI’s Nairobi campus this week.
Can our global livestock systems meet a triple bottom line—protecting health, the environment and equity? Can 14 high-level leaders and thinkers outline and agree on a strategy that can help the world fulfill on that ambitious livestock agenda to 2020? Can all this be done in one and a half days?
Three weeks after Bill Gates announced at a meeting of the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) in Rome new grants of USD200 million from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) to support the world’s smallholder farmers—a meeting in which Gates called on the big United Nations food-related agencies to work together to create a global productivity target for those small farmers—those agencies are meeting this week in Nairobi to hammer out the outlines of a consensus regarding strategies for a global livestock agenda to 2020.
This High-Level Consultation for a Global Livestock Agenda to 2020 is being co-hosted by:
Francois Le Gall, livestock advisor at the World Bank, and
Jimmy Smith, director general of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI).
The dozen other heads of institutions and departments among the world’s leading bodies for food security that are taking part are:
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
Soloman Benigno, project manager and animal health expert
AU-IBAR (African Union-Interafrican Bureau for Animal Resources)
Ahmed El-Sawalhy, director
Bruce Mukanda, senior program and projects officer
Baba Soumare, chief animal health officer
Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF)
Kristin Girvetz (formerly Grote), program officer
European Union (EU) Delegation to Kenya
Bernard Rey, head of operations
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations
Henning Steinfeld, chief of livestock information and policy
International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
Carlos Sere, chief development strategist
United Nations (UN)
David Nabarro, special representative of the UN secretary general for food security and nutrition (via filmed presentation)
World Bank
Stephane Forman, livestock specialist for Africa
World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE)
Bernard Vallat, director general
Walter Masiga, sub-regional representative for Eastern Africa and the Horn of Africa
Among the ideas rising to the surface for these leaders of global livestock departments and institutions are the need to shift focus from livestock per se to livestock-based lives and lands. The discussions are centering initially on three pillars of livestock development: health, environment and equity.
David Nabarro, the UN special representative for food security and nutrition, in a filmed presentation for this high-level consultation, said:
There is a movement for the transformation of food systems throughout the world. Livestock is an essential part of this equation. ILRI and the World Bank are key actors in seeing that science is applied for effective action for improved livestock systems. This meeting is important and happening when it should.
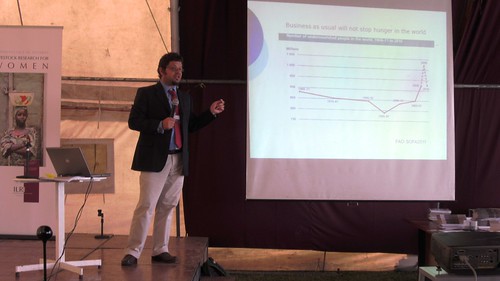
ILRI director general Jimmy Smith then gave an overview of the trends, opportunities and challenges of livestock development.
Feeding the world is possible, Smith concluded, as is sustaining our natural resource base and reducing absolute poverty.
Our challenges in achieving these, the livestock director said, include ‘improving our methodologies to develop more reliable assessments of the hard trade-offs involved in choosing ways forward for livestock development, managing those trade-offs at multiple scales, and ensuring institutional innovations, which will be as important as technological innovations—and perhaps harder to achieve’.
Watch and listen to Smith’s presentation.
Among the trends Smith highlighted are:
- Demand for livestock products continues to rise
- Livestock systems will continue to produce much of the world’s food
- There remains a vast divide between developed and developing regions in kinds of livestock systems and their costs and benefits, but those different worlds are increasingly interconnected
Smith stressed the need for more reliable evidence-based assessments of the hard trade-offs implicit in our choices for the livestock sector, which will differ greatly in different regions and circumstances, especially in light of the fact that livestock impact so many important global development issues (e.g., human health, environmental protection, global food security)
An example of how critical livestock issues are for human well-being that Smith pointed out is the interface between livestock and human health.
Animal source foods are the biggest contributor to food-borne disease, Smith said. Diseases transmitted from livestock and livestock products kill more people each year than HIV or malaria. Indeed, one new human disease emerges every 2 months; and 20 percent of these are transmitted from livestock.
This consultation on a global livestock agenda comes at an appropriate time for Jimmy Smith, who started his tenure as director general of ILRI only late last year and who has instituted a task force, headed by ILRI’s director for institutional planning Shirley Tarawali, to refresh ILRI’s long-term strategy for livestock research for development. As several of the other institutions represented at this meeting are also in the thick of rethinking their strategies, this 1.5-day intense consultation is able to harvest the fruits of much recent hard thinking that has already been done in these global and regional institutions.