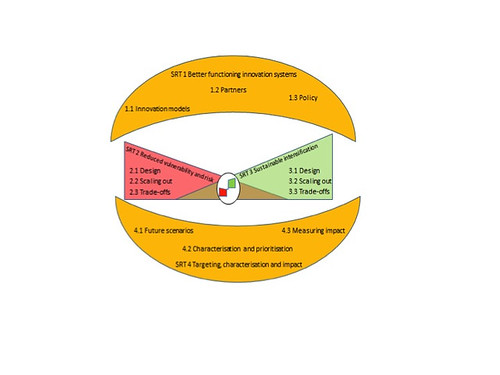
A new CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems is being planned to find ways to help dryland communities climb out of poverty while enhancing their food security and protecting their natural resources. This program will conduct four strategic research themes in five regions. Two of the research themes—reducing vulnerability/managing risk and sustainably intensifying production—make up the ‘meat’ of what has come to be called ‘the hamburger’ diagram. The top and bottom ‘buns’ represent the other two research themes: strengthening innovations systems and measuring impacts/synthesizing knowledge across regions, respectively (figure by the CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems).
This week in Nairobi, Kenya, opening on a morning as grey and cold as London’s weekend Diamond Jubilee celebrations on the Thames, a Regional Inception Workshop of the CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Agricultural Systems for East and Southern Africa is being held. The 3-day workshop (5–7 Jun) is organized and hosted by the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI). This inception workshop brings together more than 50 experts working in the drylands of eastern and southern Africa to identify key hypotheses and research questions for the research program, to agree on initial sites for its activities and to develop impact pathways and implementation plans. See the introductory slide presentation by Maarten Van Ginkel, deputy director general of the International Centre for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA): The CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems: Scientific content and progress in the inception phase.
The planners of this CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems (the full mouthful of a title of which is ‘Integrated and Sustainable Agricultural Production Systems for Improved Food Security and Livelihoods in Dry Areas’) say this large, multi-institutional, multi-stakeholder and multi-diciplinary research program aims to develop a series of complementary technologies, policies and institutional innovations that will help very poor and highly vulnerable dryland populations improve their livelihoods—and do so over the longer term.
As its full name suggests, this CGIAR research program will apply ‘integrated systems’ approaches, which focus less on technical fixes for discrete problems and more on how interventions can be combined to meet the many needs of a profitable, equitable and sustainable agricultural production system. And the program will use large, so-called ‘landscape level’ frameworks to help scientists think through the links between farm or community practices and the broader ecosystem in which they are located; such analyses should allow, for example, more comprehensive assessments of the increasingly hard trade-offs in use of natural resources.
See consultant John Lynam’s slide presentation (below), which gives a comprehensive overview of ‘systems thinking’. Lynam argued that we need to change our research designs and methods if we’re going to serve the expanding agendas for international agricultural research. In his presentation he asked asked some provocative questions, such as, ‘How do we (should we) understand system performance? Is it by productivity, profitability, or income? Is it levels of vulnerability or food security? Or is it resource efficiency or resilience?. . . . Why do we have plantain (matoke) systems in Uganda while beer banana systems dominate in Burundi and Rwanda? . . . Why are many more people exiting agriculture in Africa than they are in Asia?’
The dry areas of the developing world occupy some 3 billion hectares, which represent 41% of the earth’s land area. These drylands are home to 2.5 billion people, who make up about a third of the population in developing countries. At least 16% of this population lives in chronic poverty.
These people make a living from the drylands by growing and managing a mix of food, fodder and fibre crops; vegetables; rangeland and pasture grasses, shrubs and trees; fruit and fuel-wood trees; medicinal plants; livestock; and fish. These dryland people face enormous environmental challenges, which in many regions are likely only to worsen with climate change.
This program targets two kinds of drylands. The first are those with the deepest endemic poverty and the most marginalized and vulnerable people, the most extreme environmental variability, and often the greatest natural resource degradation as well. The second are those with the greatest potential to increase food security and reduce poverty over the short to medium terms.
Table discussions at an ILRI-hosted inception workshop for eastern and southern Africa component of the CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Agricultural Systems, 5-7 Jun 2012 (photo by ILRI/Susan MacMillan).
The future of dryland farming communities, the research planners assume, depends largely on their ability to more effectively manage risk as well as to diversify and intensify their agricultural production systems. The integrated approach the program will take should help people better manage their natural resources and improve their crop, vegetable, livestock, tree and fish production. The approach should also help facilitate for dryland communities the establishment of enabling policy environments; the provision of greater institutional support; and a more equitable distribution of, and control over, resources, access to information, livelihood opportunities and decision-making.
More specifically, this dryland research program aims to:
- prioritize agricultural systems for impact
- identify key researchable issues
- increase the efficiency and sustainability of natural resource use
- develop more resilient agricultural systems to manage risk and production variability
- promote in situ and ex situ conservation and sustainable use of dryland agrobiodiversity
- improve the productivity and profitability of dryland agricultural systems through sustainable intensification, diversification, and creation of value-added products and market links
- identify niches of importance to the most vulnerable livelihoods (even if they appear to have low marketing potential)
- address constraints faced by the most marginal farmers
- develop new partnerships and models of working together.
Dryland Systems inception workshop for East and southern Africa organizer Polly Ericksen of ILRI (left) and facilitator Constance Neely of ICRAF (photo credit: ILRI/Susan MacMillan).
The structure and process of this workshop, which is focused on eastern and southern Africa, have been developed by an interdisciplinary research team headed by ILRI’s Polly Ericksen, with participants from the World Agroforestry Centre, the International Water Management Institute and the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, as well as agricultural research consultants John Lynam and Brian Keating. The lead centre for this CGIAR research program is the International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas.
In this region, the drylands program plans to work to reduce vulnerability in three areas of three East Africa countries:
Northern Kenya/southeastern Ethiopia: the triangle from Garissa in Kenya to Borana in south-central Ethiopia to Somali Region in southeast Ethiopia
Central Kenya: Baringo District
Southern Kenya/northern Tanzania: Kajiado and Narok districts and Serengeti National Park and Monduli and Samanjiro districts.
The program plans work to intensify agricultural production in three areas of three eastern and southern African countries:
Zambia-Malawi-Mozambique: the Chinyanja Triangle
Northeast Tanzania: from Kahama through Shinyanga to Babati districts
Ethiopia: the Oromia zones of East Shoa, West Shoa, Horogudru and the Amhara zone of North Shoa
For more information, visit the website for this CGIAR Research Program.
See previous blogs about this workshop:
ILRI Clippings Blog: CGIAR Drylands Research Program sets directions for East and Southern Africa, 4 Jun 2012.
ILRI Clippings Blog: Supporting dryland pastoralism with eco-conservancies, livestock insurance and livestock-based drought interventions, 5 Jun 2012.
A set of images of this workshop are on ILRI’s Flickr site.