The Index-Based Livestock Insurance project, which works with pastoral livestock keepers in Kenya’s Marsabit District, is being highlighted in a launch on 8 July 2011 of the Kenya Government’s Open Data Web portal (photo credit: ILRI/Mude).
Andrew Mude, a scientist with the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) who leads an ‘Index-Based Livestock Insurance’ project, on 8 July 2011 will describe how his project is using satellite imagery to provide the first livestock insurance to pastoral livestock herders in Kenya’s northern drylands. He is making this presentation at the launch of a new Kenya Government Open Data Web portal. The launch will be opened by Kenya President Mwai Kibaki at the Kenyatta International Conference Centre, in Nairobi’s city centre.
The Index-Based Livestock Insurance project is a novel scheme that provides livestock insurance against animal losses to over 2000 households in Kenya’s Marsabit District. This insurance product, the first to ever be offered in the district, is helping livestock keepers to sustain their livelihoods during droughts. The project was started by ILRI in partnership with UAP insurance and Equity Bank, along with other partners, in January 2010.
The new Kenya Government Open Data Web portal is one of the first in sub-Saharan Africa and it will, for the first time, make several large government datasets available to the public in an easy to search and view format. The portal will allow Kenyans to search and display national and county-level data in graphs and maps and allow for easy comparison and analysis of information.
The launch of Kenya Government Open Web portal is also bringing together over 30 exhibitors who will showcase their use of technology to share information. ILRI has an exhibit showcasing its Index-Based Livestock Insurance project.
Use of open-source technology to store, analyze, manage and display data is on the rise in Kenya and recently received a boost with the launching of Virtual Kenya, a new website that hosts maps and spatial data about the country, making them available for use by citizens. Started by Upande Ltd., a Nairobi-based technology company, Virtual Kenya, has expressed interest in hosting some of the data generated by ILRI’s Index-Based Livestock Insurance project to demonstrate how open-source technologies are improving information access in the country.
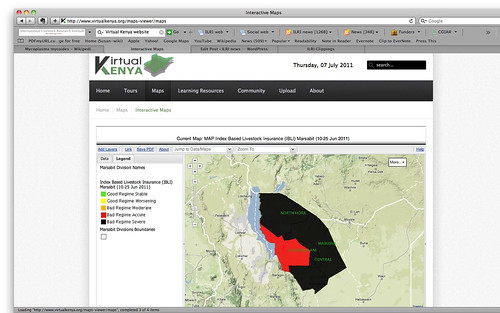
Map showing the critically low forage availability in Kenya’s Marsabit District in June 2011; the entire district is at acute (red) to severe (black) low levels of forage to feed the district’s many livestock (map by ILRI’s Index-Based Livestock Insurance project and made available on the Virtual Kenya website).
One such map generated by data from the Index-Based Livestock Insurance project is already available on the Virtual Kenya website. The map shows viewers that in the current severe drought affecting northern Kenya, as well as southern Ethiopia and Somalia, throughout Marsabit District livestock forage availability is at acutely to severely low levels. That is, the amount of forage available to feed the pastoral livestock herds that support most people’s livelihoods in this district is significantly below long-run averages for this time of year, indicating that many of the domesticated livestock are expected to starve. (The next rains in the region are not due until October.)
In April 2011, ILRI’s Index-Based Livestock Insurance project won the Vision 2030 ICT Innovation Award for ‘the overall best innovation for their mobile-ICT-based livestock insurance solution.’ This award event was organized by the Kenya ICT board and the Kenya Vision 2030 Delivery Secretariat, which said the ILRI project was ‘a promising and exciting innovation in insurance design that allows the risk-management benefits of insurance to be made available to poor and remote clients.’
The Index-Based Livestock Insurance project also won a best-practice award from the Poverty Reduction, Equity and Growth Network in recognition of its innovative approach in combining scientific research and practical solutions; that award was bestowed in September 2010 in South Africa.
To find out more about the Open Data Web portal, visit the Kenya ICT board website: http://www.ict.go.ke/