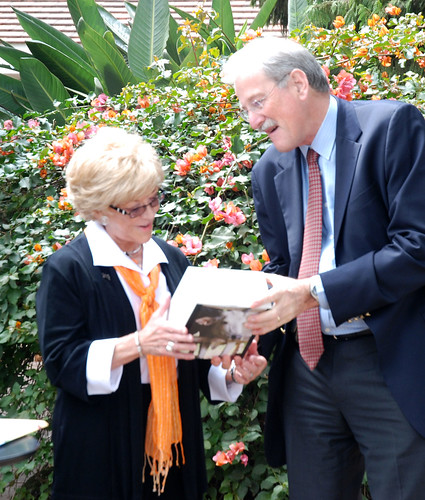
The World Food Prize, known as the ‘Nobel for Food’ (no Nobel Prize exists for agricultural science), was created in 1986 by Norman Borlaug, who himself won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work creating high-yielding crop varieties estimated to have saved more than 1 billion lives from famine. The World Food Prize honours those who improve the quality, quantity or availability of food in the world. A co-winner of this year’s World Food Prize, announced on 16 June by US Secretary of State Hilary Rodham Clinton, is Jo Luck, president of the popular American charity Heifer International, which provides farm animals to needy families, who then ‘pass on’ the gift of subsequent offspring to others in need.
Speaking in a seminar held in her honour at the Nairobi campus of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), where she served as a member of ILRI’s Board of Trustees between 2002 and 2005, Jo Luck reflected on her life that was a preparation for the role she now plays. ‘All the time I was learning what has brought me to this road. My experiences as a teacher and as a parent taught me how to recognize both the strong and the weak and how to bring people together and empower them by listening and learning from them,’ she said.
‘I represent many people who are receiving this award through me and I hope to honour and represent them properly,’ she said.
Those lucky enough to meet Jo Luck are struck immediately, and almost physically, by the depth of her energy and passion. Her ability to quickly tell a moving story that inspires people to make a difference in the world has more in common with, say, Oprah Winfrey (who has interviewed Jo Luck on her show) or Bill Clinton (who Jo Luck used to work for) than with other heads of charitable or development organizations.
The results of much of Jo Luck’s life’s work can be seen in communities in the developing world. Since joining Heifer in 1992, she has vastly up-scaled Heifer’s programs, which provide food- and income-producing animals to poor families, and helped broaden Heifer’s agenda, which now includes improving livelihoods through education and community development as well as animal husbandry.
With skilful management and superb communications abilities, Jo Luck built innovative educational initiatives that link grassroots donors in rich countries to recipients in developing countries. This not only brought new (and renewable) resources to poor farmers in developing countries but also gave Americans much better understanding of global hunger and poverty issues. As a result of her efforts, both the scope and impact of Heifer International have grown throughout Africa, the Americas, Asia, the South Pacific and Central and Eastern Europe. At least 10 million families, including 1.5 million families in 2009 alone, have been helped both to put nutritious food on their own tables and to feed others.
Carlos Seré, ILRI’s Director General, said that recognition of Jo Luck’s work with Heifer International ‘shows not only that a committed individual can make a difference in addressing global poverty and food insecurity, but also how much livestock matter and to how many people—animals help some one billion people to sustain their livelihoods and helps many of those to escape poverty.’
‘Jo Luck has impacted world poverty through gifts of livestock’, Seré said. ‘Cows, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens, camels and other farmed animals provide poor households with a means of livelihood, with sustenance and with the regular income needed to educate their children, enabling them to finally escape the poverty trap.’
But Jo Luck emphasized that gifts of animal stock, however welcome, are not enough. ‘Livestock production cannot be made sustainable without understanding the environment,’ she said. And this is where she believes researchers, policymakers, government officials and others need to come together. ‘We need to ensure not only that the animals poor people depend on are healthy and productive but also that this livestock productivity can be sustained over the long term without harming the environments of poor communities.’
Jo Luck has worked with ILRI and other groups to bring about closer collaboration between experts and local communities. Such collaboration, for example, is at the heart of a Heifer-run East African Dairy Development Project being conducted in Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda. ILRI works with Heifer on this project along with TechnoServe, ABS-TCM and World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF). ILRI researchers are providing technical advice on such matters as improved breeding and feeding and are monitoring and evaluating the project as it goes along. This project, which is creating dairy ‘hubs’ in the three countries, is helping 180,000 households to participate in, and profit from, a booming dairy industry in East Africa. By joining forces, the partners in this project aim to help one million people, mostly poor rural farmers, double their incomes in the next few years.
The key to such collaboration, Jo Luck says, is simple. ‘We work directly with the people we mean to serve. We listen to them and learn from them. They make their own decisions about what works best for them. We then seek the resources that will let them fulfil their goals.’
Jo Luck will receive the 2010 World Food Prize in Des Moines, Iowa, on 14 October this year. Both she and her co-winner, David Beckmann, President of Bread for the World, another American grassroots organization working to end world poverty and hunger, will make presentations at the event, as will ILRI Director General Carlos Seré and other leading heads of international development work.
For more information about Jo Luck’s work with Heifer please read this related article.
In the following two short video interviews, Jo Luck discusses 'how livestock catalyze community development' and 'delivering livestock research that makes a difference'.
The World Food Prize website has further information about the Laureate Award Ceremony and Borlaug Symposium.