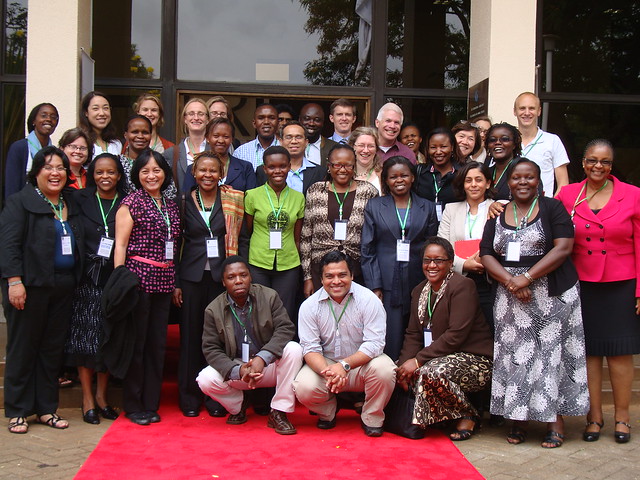
RED CARPET WELCOME: His Excellency Mwai Kibaki, President of the Republic of Kenya, generously allowed his presidential red carpet to be briefly used for a photograph of a group of pro-women agricultural scientists this month at the International Livestock Research Institute (photo credit: ILRI/MacMillan).
Unusually, and, if truth be said, thrillingly, the Nairobi headquarters of the International Livestock Research Institute and BecA—a Biosciences eastern and central Africa Hub that ILRI hosts and manages—have, within the space of 12 months, been visited by two very seriously important persons: Bill Gates, co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, in early December 2009; and Mwai Kibaki, president of the Republic of Kenya, early this month (November 2010).
Biotech men
Both VIPs expressed excitement in, and support for, BecA’s recently launched state-of-the-art biosciences facilities, which they happily toured, donning crisp white lab coats to inspect BecA’s ultra-modern, super-molecular laboratories, including a half-million-dollar ‘454’ DNA sequencer, a space-agey-looking biosafety containment facility and a shiny brand-new greenhouse.

BILL GATES, Co-Chair of the Bill and Melinda Gates foundation and former CEO of Microsoft, toured the ultra-modern laboratories of BecA at ILRI last December (2009) (photo credit: ILRI/Ouma).

HIS EXCELLENCY Kenya President Mwai Kibaki on a tour of the same labs this November (2010), led by BecA Hub Director Segenet Kelemu (third from left) (photo credit: ILRI/Masi).
The feminization of biotech
While the entourages of both Gates (who was on a private visit) and Kibaki (on a State visit) were mostly male, BecA’s director, Ethiopian Segenet Kelemu; as well as a key initiator and supporter of BecA, Australian Gabrielle Persley; and some half the students and African scientists the VIPs met and interviewed while they toured the labs, were female. On both visits, our male VIPs appeared impressed by the high 'girl power' in these high-tech labs. And so they should have been, both VIPs coming of age (Gates is 55 this year, Kibaki, 79) when such visible expression of the closing of the gender gap was rare.

POLITICIANS AND SCIENTISTS: Segenet Kelemu, director of the BecA Hub at ILRI, explains to President Kibaki the significance of a metal and glass sculpture of a DNA helix unveiled by the president at the official opening of the Hub earlier this month (5 November 2010) (photo credit: ILRI/Njuguna).
Closing the gender gap
Fortuitously and aptly, then, on the morning of President Kibaki’s visit to ILRI on 5 November 2010 to officially open the BecA Hub, another meeting, arranged by research groups much earlier than the State visit was arranged, was starting in another venue on the same ILRI campus, far from the imposing presidential dais, marching band, schoolgirl choir and guest and refreshment tents erected and assembled down the hill, in front of ILRI’s Mara House office building.
Back up the hill, then, in a meeting room adjacent to a quiet quad and out of the fray, a group of (mostly) women experts on gender and agriculture in developing countries opened an ‘inception’ workshop for a new scientific project aiming to reduce inequalities between men and women (and boys and girls) in agricultural development.
We know that Bill Gates supports this work, because his Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation is funding the project. And we suspect that President Kibaki would also be supportive. (Upon learning that a schoolgirl choir, standing near the presidential dais, had awaited his arrival from the labs for several hours to sing for him, Kibaki admonished his staff that the girls ought to be in school, this being a Friday, and instructed them to have all the schoolgirls immediately seated under the tents.)

GIRL POWER: A schoolgirl choir walks past one of several red carpets laid out in honour of a visit to BecA and ILRI by President Mwai Kibaki (photo credit: ILRI/MacMillan).
Historic beginnings for closing the gender gap in agricultural projects
The gender research project being quietly kicked off in ILRI’s N’Dama Lounge was, in its way, as much an historic beginning as the advanced labs being opened further down the hill. Scientists at ILRI and elsewhere have known for years that more—much, much, much more—should be done to address women’s issues in agricultural development. And they have struggled for years to incorporate women’s issues into their research programs. With little success.
Women continue to have fewer assets than men
If small-scale agriculture remains the backbone of most developing-country economies, women remain the stuff that makes up that backbone. Across nationalities, cultures and religions, women more than men tend to invest their time and energy and income in the stuff that matters most to most of us, with the greatest benefits provided to the greatest numbers of poor. Yet women have fewer assets than men—whether we look at land, natural resources and other tangible assets or less tangible ones like human capital. This gap between men’s and women’s assets not only reduces agricultural productivity, but also restricts women’s decison-making power, which affects such vital matters as sustainable food production, children’s nutrition and education, and economic development.
That’s what we know. Not what we do. And the disconnect between what we know to do in ‘gender’ issues in agricultural development and what we do do has been getting bigger and more glaring every year.
When pigs fly, we used to say, not so long ago, we will all be working to help women help the rest of us in development—just because that’s what women tend to do, regardless of their material circumstances. The disjunct between what women do for agriculture and what we in agricultural research and development do for them, we said, was a disgrace. And then we would sigh and crawl back into a ‘what to do?’ cynicism. What our staff lacked, we said, was the training and technical assistance needed first to identify and then to address disparities in agricultural development and in assets. That’s now changing. At ILRI the change is due to the institute’s recent hiring of people who know what to do—and are ready to do it.
These new staff and positions include some of the best scientists in the world who are champions of gender research in agricultural development. These relatively new ILRI staff include Jemimah Njuki, a Kenyan leading sociologist in gender and agriculture studies; Nancy Johnson, an American agricultural economist and poverty analyst; and Canadian Patti Kristjanson, a long-term ILRI economist who just two years ago launched a 'Women and Livestock Challenge Dialogue'. (In January of this year, Kristjanson moved to the World Agroforestry Centre, across town from ILRI, to lead a research team that is part of a new global climate change initiative involving all 15 centres of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research, to which ILRI belongs.) These three women formed a Gender, Poverty and Impacts research team which, despite starting only one-and-a-half years ago, has already created the momentum across ILRI for re-focusing on gender and agriculture.

ILRI PUTS WOMEN'S ISSUES FRONT AND CENTRE: Jemimah Njuki, a Kenyan expert in gender and agriculture and impact analysis working for ILRI, waits with ILRI's deputy director general-research John McDermott, a Canadian veterinary researcher, beside the red carpet laid down at ILRI's entrance for the presidential visit happening at the same time, in front of an office building down below (photo credit: ILRI/MacMillan).
Can a few women make a difference?
Can a few committed women and some supportive men make a big difference in gender research for development? With institutional support, we're betting on it. ILRI’s seriousness about, and new serious expertise in, empowering women farmers and marketers got the attention of other groups working toward the same goal. The ILRI group has joined forces with the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) team of Ruth Meinzen-Dick and Agnes Quisumbing, long-time researchers on gender and agriculture.
This inception workshop for the ‘Gender, Agriculture and Assets Project,’ held from 5–7 November 2010, is a 3-year initiative of IFPRI and ILRI funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. The overall aim of the initiative is to improve rural livelihoods in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia by helping agricultural development programs significantly reduce inequalities, including disparities in assets, between men and women.
The workshop brought together research and development partners from different organizations. In addition to IFPRI and ILRI, these included BRAC, CARE Bangladesh, East Africa Dairy Development project, Fintrac Inc, Grameen Foundation, Helen Keller International, International Rice Research Institute, Kickstart International, Land O’Lakes, Rural Development Institute, Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility initiative at the International Center for Tropical Agriculture, and the World Vegetable Centre (AVDRC), as well as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the International Fund for Agricultural Development and the United States Agency for International Development.
As part of the initiative, the team will evaluate some 10 agricultural research and development projects funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the United States Agency for International Development, the World Bank, and others to identify the impacts of these projects on women’s assets and to clarify which strategies have been successful in reducing gaps between men and women in access to, and control of, assets.

THINKING BIG: IFPRI's Ruth Meinzen-Dick gives an overview of the ambitious aims of the Gender Assets Gaps project (photo credit: ILRI/MacMillan).
The project is based on several premises: (1) that control over, and ownership of, assets is a critical component of well-being, (2) that increasing control or ownership of assets does more to help create pathways out of poverty than increasing incomes or consumption alone and (3) that the different kinds of assets addressed by a project—whether tangible or intangible, for example, or whether defined as natural, physical, financial, human, social or political ‘capital’—matter. Project staff are investigating the control of assets because who controls assets in households matters a lot. Household members typically do not pool all resources or agree on what their scarce resources should be used for. The benefits of policy changes in any given household or community are determined largely by who in the household or community is the main beneficiary of the new resources. And we now have evidence from many countries that increasing the resources under the control of women not only improves the nutrition and health of children, but also increases agricultural productivity and household incomes.
Astonishingly, although women make a significant contribution to agriculture in developing countries and are much more likely than men to use their (scarce) resources to improve the nutrition, welfare and well-being of their families, they are still neglected in most agricultural research and development programs. At a Global Conference on Agricultural Research for Development, held in Montpellier, France, last March (2010), IFPRI’s Ruth Meinzen-Dick argued that accounting for gender in our research and development work is not an option but a necessity if we are going to reduce world poverty and feed the world’s growing populations (which are expected to peak at mid-century, falling after that): ‘Changing agricultural research and development from male-dominated to gender-equitable is not merely an issue of political correctness or ideology; it is a matter of development effectiveness that can benefit everyone.’
Although getting reliable, accurate and timely statistics disaggregated by gender remains a formidable challenge for most countries (in 2010, the United Nations found that no census had been carried out in the last three decades in 41 per cent of the countries in sub-Saharan Africa), what we know is probably enough to be getting on with. The following should give a flavour of the depth and scope of the issues.
More women than men:
- own no land
- are poor and hungry
- are illiterate
- are refugees
- are living with HIV (in Africa)
- are caring for those living with HIV/AIDS.
Most women:
- work longer hours than men
- work in jobs with lower pay, status, power and authority than men
- get paid less than men for doing the same work
- provide most of the family labour and are unpaid for that labour
- bear double responsibility for household and farm work
- receive a fraction of the agricultural extension and support services provided to men
- have half the education levels of men
- have less access to health care services than men
- have fewer legal rights than men.
Flying pigs?
Fortunately, as detailed and dissected in this inception workshop, projects from South Asia (Bangladesh, India, Nepal) and sub-Saharan Africa (Burkina Faso, Cameroon, DR Congo, Ghana, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Nigeria, Uganda, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Zimbabwe) have potential to address such asset disparities.
These projects are working across the spectrum of women’s rural livelihoods and concerns in these regions, from animal husbandry to vegetable genetics, from nutrition and sociology to agricultural economics and development management. An enumeration of some of the more obvious specific topics tackled in the projects presented at this workshop gives some idea of the broad disciplinary expertise demanded by those working to help women use agriculture to better their lives. These include dairy development, land transfer to girls, vegetable production, development and dissemination of nutrient-rich foods such as orange-fleshed sweet potatoes, value addition and processing, market information systems, high-value horticulture, crop management and irrigation.
Some of the opportunities described in overviews of these projects include the following.
- Fully 94 per cent of the vendors in vegetable markets in sub-Saharan Africa are women.
- Twice as many women as men in Uganda cultivate sweet potatoes, most sweet potato traders in towns as well as villages are women, and women tend to be less risk-averse in crop choice than men.
- Contrary to previous reports, information tips delivered by mobile phone delivery of market and other agricultural information in Uganda show female farmers are very interested in receiving, and acting on, timely market information.
- Legumes, once considered a 'woman's crop in much of Africa, can directly benefit the nutrition of poor households.
- With increasing migration of men from rural to urban areas in South Asia, the roles of women are shifting from unpaid farm labourers to de facto farm managers.
- Seedling nurseries are an opportunity for women because they require relatively little labour and can be established close to homesteads.
- East African women dairy producers have most control of the milk they sell informally in the evening.
According to this group of scientists, the gender research areas in greatest need of addressing are:
- Training in methods to integrate gender and asset-based approaches in agriculture development programs.
- Evaluating agriculture development programs to understand what works and what does not work in building women’s assets and scaling out those strategies that work.
- Collecting gender-disaggregated data.
- Initiating, and training in, gender-sensitive monitoring and evaluation work.
- Expanding measurements of income and consumption to include evaluations of how projects build assets.
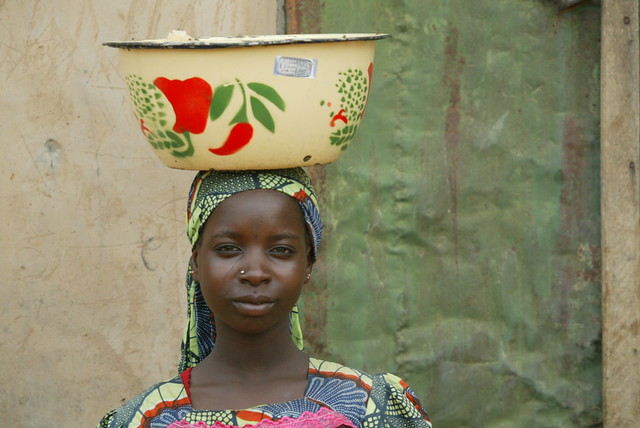

THE TARGET, THE BENEFICIARY, THE HOPE: A young girl sells food to villagers outside Kano, Nigeria (photo credit: ILRI/Mann).
The gender and agricultural assets initiative wants to learn from the most promising successes in these projects so as to help redress imbalances in power. The project leaders are dreaming and thinking big. They aim no less than pushing a ‘paradigm shift’ in agricultural development programming from ‘gender exploitive’ to ‘gender accommodating’ to ‘gender transformative’. This will of necessity mean taking on a lot, including ‘challenging the ideological, socio-cultural, economic, political and institutional frameworks and structures that create and recreate gender inequalities’. The project leaders are well aware of the danger that such targeting, if not done well, can lead to a backlash that further marginalizes rather than supports poor women. And they recognize the role of men in achieving gender equality.
This project will train teams of experts in how to use tools to assess the assets held by men, women and households as a whole and in how to integrate and measure the effectiveness of strategies for increasing the assets of women. To this end, IFPRI’s Ruth Meinzen-Dick proposed a conceptual framework for analyzing assets while ILRI’s Jemimah Njuki presented different strategies for addressing gender in agricultural programs, explaining why and how to complement quantitative tools in monitoring and evaluation with qualitative tools. IFPRI’s Dan Gilligan described methods for evaluating quantitative impacts and ILRI’s Nancy Johnson and IFPRI’s Agnes Quisumbing discussed different types of assets, data needs and data collection instruments. Project implementers and evaluators in this initiative are expected to work hand in hand over the life of the selected projects, using both qualitative and quantitative methods to assess and document changes from baselines in levels of control and ownerships of assets.
And pigs, then, will perhaps have a chance to start to fly.
For more information, visit, the following:
http://agrigender.wordpress.com/
http://www.slideshare.net/genderassets/slideshows
https://www.flickr.com/photos/ilri/sets/72157625322903538/
http://agrigender.wordpress.com/2010/10/27/workshop-on-gender-and-market-oriented-agriculture-revised-dates/
Announcement of a forthcoming TEDx event at IFPRI, on 14 Devember 2010, in Washington, DC, with talks by ILRI’s Jemimah Njuki and IFPRI’s Agnes Quisumbing and Ruth Meinzen-Dick on gender as the ‘missing ingredient’ in many development policies and programs:
http://genderassets.wordpress.com/2010/11/07/upcoming-tedx-event-on-gender/
A filmed presentation by ILRI’s Jemimah Njiki making the case that animal agriculture can be used to help redress skewed resources available to rural women worldwide (in societies where women are unable to own anything else, farm animals provide women with incomes; and when those women’s incomes rise, the health, nutrition and education of their whole families also rise, with everybody winning):
http://ilri.blip.tv/file/3418393/