Research released at conference calls for thinking through the health impacts of agricultural intensification to control epidemics that are decimating herds and endangering humans (Picture credit: ILRI/Mann).
Increasing numbers of domestic livestock and more resource-intensive production methods are encouraging animal epidemics around the world, a problem that is particularly acute in developing countries, where livestock diseases present a growing threat to the food security of already vulnerable populations, according to new assessments reported today at the International Conference on Leveraging Agriculture for Improving Nutrition & Health in New Delhi, India.
‘Wealthy countries are effectively dealing with livestock diseases, but in Africa and Asia, the capacity of veterinary services to track and control outbreaks is lagging dangerously behind livestock intensification,’ said John McDermott, deputy director general for research at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), which spearheaded the work. ‘This lack of capacity is particularly dangerous because many poor people in the world still rely on farm animals to feed their families, while rising demand for meat, milk and eggs among urban consumers in the developing world is fueling a rapid intensification of livestock production.’
The global conference (http://2020conference.ifpri.info), organized by the International Food Policy Research Institute, brings together leading agriculture, nutrition and health experts to assess ways to increase agriculture’s contribution to better nutrition and health for the world’s most vulnerable people.
The new assessments from ILRI spell out how livestock diseases present ‘double trouble’ in poor countries. First, livestock diseases imperil food security in the developing world (where some 700 million people keep farm animals and up to 40 percent of household income depends on them) by reducing the availability of a critical source of protein. Second, animal diseases also threaten human health directly when viruses such as the bird flu (H5N1), SARS and Nipah viruses ‘jump’ from their livestock hosts into human populations.
McDermott is a co-author with Delia Grace, a veterinary and food safety researcher at ILRI, of a chapter on livestock epidemics in a new book called ‘Handbook of Hazards and Disaster Risk Reduction.’ This chapter focuses on animal plagues that primarily affect livestock operations—as opposed to human populations—and that are particularly devastating in the developing world.
‘In the poorest regions of the world, livestock plagues that were better controlled in the past are regaining ground,’ they warn, with ‘lethal and devastating impacts’ on livestock and the farmers and traders that depend on them. These ‘population-decimating plagues’ include diseases that kill both people and their animals and destroy livelihoods.
Livestock-specific diseases include contagious bovine ‘lung plague’ of cattle, buffalo and yaks, peste des petits ruminants (an acute respiratory ailment of goats and sheep), swine fever (‘hog cholera’) and Newcastle disease (a highly infectious disease of domestic poultry and wild birds). The world’s livestock plagues also include avian influenza (bird flu) and other ‘zoonotic’ diseases, which, being transmissible between animals and people, directly threaten human as well as animal health.
McDermott and Grace warn that new trends, including rapid urbanization and climate change, could act as ‘wild cards,’ altering the present distribution of diseases, sometimes ‘dramatically for the worse.’ The authors say developing countries need to speed up their testing and adoption of new approaches, appropriate for their development context, to detect and then to stop or contain livestock epidemics before they become widespread.
In a separate but related policy analysis to be presented at the New Delhi conference, McDermott and Grace focus on links between agricultural intensification and the spread of zoonotic diseases. The researchers warn of a dangerous disconnect: the agricultural intensification now being pursued in the developing world, they say, is typically focused on increasing food production and profitability, while potential effects on human health remain ‘largely ignored.’
A remarkable 61 percent of all human pathogens, and 75 percent of new human pathogens, are transmitted by animals, and some of the most lethal bugs affecting humans originate in our domesticated animals. Notable examples of zoonotic diseases include avian influenza, whose spread was primarily caused by domesticated birds; and the Nipah virus infection, which causes influenza-like symptoms, often followed by inflammation of the brain and death, and which spilled over to people from pigs kept in greater densities by smallholders.
The spread and subsequent establishment of avian influenza in previously disease-free countries, such as Indonesia, was a classic example, McDermott and Grace say, of the risks posed by high-density chicken and duck operations and long poultry ‘value chains,’ as well as the rapid global movement of both people and livestock. In addition, large-scale irrigation aimed at boosting agricultural productivity, they say, has created conditions that facilitate the establishment of the Rift Valley fever virus in new regions, with occasional outbreaks killing hundreds of people along with thousands of animals.
The economic impacts of such zoonotic diseases are enormous. The World Bank estimates that if avian influenza becomes transmissible from human to human, the potential cost of a resulting pandemic could be USD3 trillion. Rich countries are better equipped than poor countries to cope with new diseases—and they are investing heavily in global surveillance and risk reduction activities—but no one is spared the threat as growing numbers of livestock and easy movement across borders increase the chances of global pandemics.
But while absolute economic losses from livestock diseases are greater in rich countries, the impact on the health and livelihoods of people is worse in poor countries. McDermott and Grace point out, for example, that zoonotic diseases and food-borne illnesses associated with livestock account for at least 16 percent of the infectious disease burden in low-income countries, compared to just 4 percent in high-income nations.
Yet despite the great threats posed by livestock diseases, McDermott and Grace see a need for a more intelligent response to outbreaks that considers the local disease context as well as the livelihoods of people. They observe that ‘while few argue that disease control is a bad thing, recent experiences remind us that, if livestock epidemics have negative impacts, so too can the actions taken to control or prevent them.’
An exclusive focus on avian influenza preparedness activities in Africa relative to other more important disease concerns, they point out, invested scarce financial resources to focus on a disease that, due to a low-density of chicken operations and scarcity of domestic ducks, is unlikely to do great damage to much of the continent. And they argue that a wholesale slaughter of pigs in Cairo instituted after an outbreak of H1N1 was ‘costly and epidemiologically pointless’ because the disease was already being spread ‘by human-to-human transmission.’
McDermott and Grace conclude that to build surveillance systems able to detect animal disease outbreaks in their earliest stages, developing countries will need to work across sectors, integrating veterinary, medical, and environmental expertise in ‘one-health’ approaches to assessing, prioritizing and managing the risks posed by livestock diseases.
—
More information on why animals matter to health and nutrition: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/3152 and https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/3149
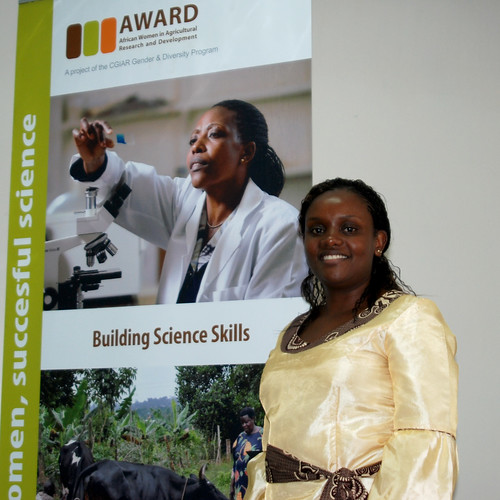
 Together with Lillian Wambua and Nimmo Gacheru, Racheal Aye (pictured) was one of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) scientists among 70 African women agricultural researchers selected for the 2011 fellowships of the African Women in Agricultural Research and Development (AWARD), which were announced on Thursday 18 August at Jacaranda Hotel in Nairobi. AWARD is an initiative of the Gender and Diversity program of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR).
Together with Lillian Wambua and Nimmo Gacheru, Racheal Aye (pictured) was one of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) scientists among 70 African women agricultural researchers selected for the 2011 fellowships of the African Women in Agricultural Research and Development (AWARD), which were announced on Thursday 18 August at Jacaranda Hotel in Nairobi. AWARD is an initiative of the Gender and Diversity program of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR).