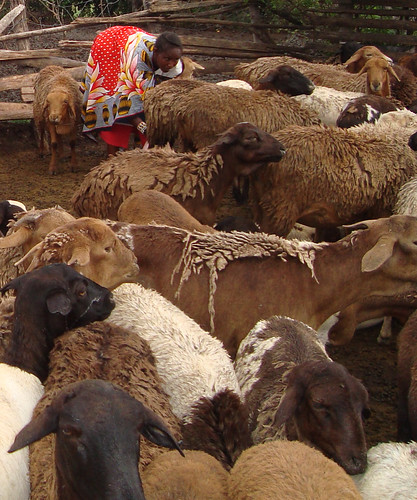
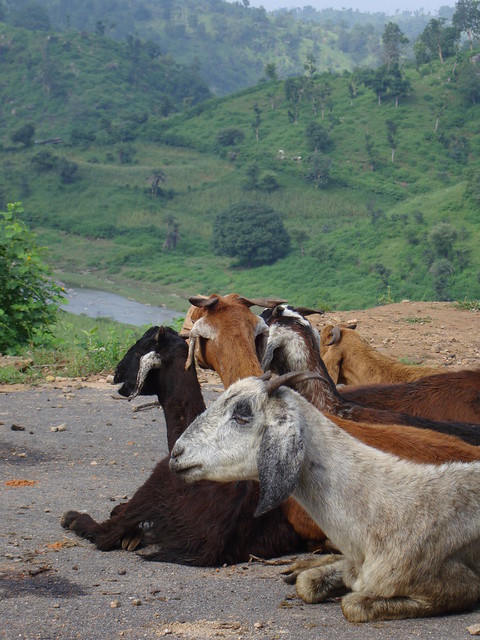
In much of sub-Saharan Africa and south Asia, people rely on both crops and animals for their livelihoods; to cope with a warmer and more variable climate, these farmers will need crop varieties and livestock breeds that can withstand droughts and floods and new diseases; where cropping becomes risky, people will rely more on their livestock than on their crops to feed themselves and make a living; on drying rangelands, many people will switch from cattle- and sheep-keeping to goats and camels, which can remain productive where there is scarce feed and water (photo credit: ILRI/Mann).
A new research program on 'Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security' (CCAFS) was launched this week.
It will link much of the best climate-related agricultural research for development work going on at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) and 14 other centres in the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) with the best global environmental change research being undertaken within the global Earth System Science Partnership.
ILRI is a key partner in this initiative, hosting the new program’s facilitator for the East Africa region, James Kinyangi. ILRI is also home to two CCAFS scientists-–Philip Thornton, who leads the ‘Integrating Knowledge for Decision Making’ theme at CCAFS, and Wiebke Foerch, an agricultural and social scientist working on food security, vulnerability and resilience of smallholders to global change. In addition, Mario Herrero, who leads ILRI’s Sustainable Livestock Futures research area, has been instrumental in supporting CCAFS as it makes the challenging transition from a CGIAR Challenge Program as originally envisioned, to this innovative and large new research program of the Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centres.
This new program is the most comprehensive to date seeking to ensure that food security is not crippled by climate change. The leaders of the new program say that urgent action is needed to help poor people adapt to climate shifts that have ominous implications for Africa and Asia.
Amidst growing alarm that climate change could deal a catastrophic blow to food security in poor countries, a partnership of the world’s premiere experts on agriculture, climate, and the environment today announced an intensive global response to confront the impacts of shifting weather patterns on crop and livestock production and their dire consequences for food security.
By 2020, the effort aims to reduce poverty by 10 per cent in the targeted regions; reduce the number of rural poor who are malnourished by 25 per cent; and help farmers in developing countries contribute to climate change mitigation by either enhancing storage or reducing greenhouse gas emissions by an amount equivalent to 1,000 million tons over a decade, compared with a 'business-as-usual' scenario.
The CCAFS program will be formally launched on 4 December at Agriculture and Rural Development Day at a United Nations climate change meeting. It is the most comprehensive effort undertaken thus far to address the interactions between climate change and food security, livelihoods and environmental management. Emerging from new collaboration between the CGIAR and the Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP), the program brings together strategic research carried out by the CGIAR, ESSP and their respective partners in a collective effort to be coordinated by the Colombia-based International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT).
The launch of CCAFS marks the beginning of a long-term endeavor with an initial 3-year budget totaling US$206 million. By building on current research for development and funding and by attracting new scientific collaboration and financial support, the program will go far toward its goal of achieving sustainable food security in the face of climate change.
Research finds that stressed agriculture systems in Africa are highly vulnerable, with studies predicting climate shifts could dramatically reduce crop yields and incomes with smallholder farmers in struggling developing countries bearing the brunt of the impact. In Asia, there are studies warning of changes in monsoon, glacier and snowmelt in areas already facing stiff competition for water resources. In Asia’s populated and intensely-farmed coastal zones, rising sea levels threaten the viability of fertile croplands.
CCAFS partners will identify and test climate change adaptation and mitigation practices, technologies, and policies that are suitable for poor, smallholder farmers and other stakeholders affected by climate change.
They will also identify 'hot spots' where intervention is urgent and conduct vulnerability assessments. In addition, they will refine models that predict the impacts of a changing climate on agriculture and livelihoods, and identify ways to select crop varieties and livestock breeds with essential traits and novel farming and food systems suitable for future climate conditions.
Partners will further help farmers deal with changes in plant, pest and disease pressures, which are particularly likely in areas where temperatures are rising, and—in collaboration with other critical actors in the food system—they will conduct research on adaptation and mitigation policies that can enhance food security.
Much of the work on the ground will begin in 2011 with an initial focus on East and West Africa and the agricultural regions of south Asia known as the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
Early 'wins' include securing a major role for agriculture in the post-2012 international climate change regime and establishing a global network of data collection sites that can help identify options for adapting to climate change.
To be held alongside the United Nations Conference on Climate Change taking place in Cancún, Mexico, Agriculture and Rural Development Day will convene some 500 policymakers, farmers, scientists and development experts who will seek to identify climate change solutions in agriculture and move this key sector to the forefront of international climate debate.
QUOTES
LE PAGE: 'Farmers have shown a remarkable ability over the centuries to adapt to climate uncertainty, but rapidly rising temperatures and associated unpredictable weather could push more vulnerable small farmers beyond their current ability to cope with the coming changes in crop cycles and in disease, insect and weed pressures,' said Lloyd Le Page, chief executive officer of the Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centres. 'That’s why we’re bringing together the world’s best scientists, and finding new ways for them to work together with farmers and decision-makers to deliver innovation and knowledge that will help solve these challenges.'
ANDERSEN: 'This new collaborative program represents a bold and innovative response to the challenge of adapting agriculture to climate change and variability while realizing the opportunities open to farmers for mitigating global warming,” said Inger Andersen, CGIAR Fund Chair and Vice President for Sustainable Development at the World Bank. 'It goes far beyond current activities, marking a new phase in our efforts to cope with climate change in agriculture through cutting- edge collaborative science.'
CAMPBELL: 'The CGIAR centers have always worked to help farmers in poor countries cope with challenging conditions by providing drought-tolerant crops or better soil and water management strategies,' said Bruce Campbell, CCAFS Director. 'But climate change threatens to alter growing conditions so rapidly and dramatically as to require an intensive effort that draws on the combined talents of all of our centers and partners. We want to bring a sense of urgency to finding and implementing solutions and attracting more support for this effort.'
LEEMANS: 'The collaboration between the CGIAR scientists and the ESSP scholars is unique in bringing together two different and separate but highly skilled research communities that cover basic and applied research on development, sustainability and environmental change,' said Rik Leemans, chair of the scientific steering committee of the ESSP. 'Sharing and joining our resources will unquestionably result in innovative ways to mitigate and adapt to climate change and simultaneously provide successful incentives to advance development.'
Listen to a news conference with the leaders of the CCAFS program.
Visit the CCAFS website and blog.
ABOUT CCAFS
The program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) is a strategic partnership of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) and the Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP). CCAFS brings together the world’s best researchers in agricultural science, development research, climate science, and Earth System science, to identify and address the most important interactions, synergies and tradeoffs between climate change, agriculture and food security. For more information, visit www.ccafs.cgiar.org.
ABOUT CGIAR
The Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) is a global partnership that unites organizations engaged in research for sustainable development with the funders of this work. The funders include developing and industrialized country governments, foundations, and international and regional organizations. The work they support is carried out by 15 members of the Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centers, in close collaboration with hundreds of partner organizations, including national and regional research institutes, civil society organizations, academia, and the private sector. www.cgiar.org – http://cgiarconsortium.cgxchange.org.
ABOUT ESSP
The Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP) was established in 2001 to promote cooperation for the integrated study of the Earth system, the changes that are occurring to the system and the implications of these changes for global sustainability. Brings together global environmental change researchers worldwide, the ESSP comprises four international global environmental change research programmes: DIVERSITAS, specialising in biodiversity and agro- biodiversity; the International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change (IHDP), specialising in institutional, socioeconomic and human security issues related to global environmental change and the policies to address it; the International Geosphere–Biosphere Programme (IGBP), specializing in the physical, chemical and biological processes that define Earth system dynamics; and the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), specializing in climate science.