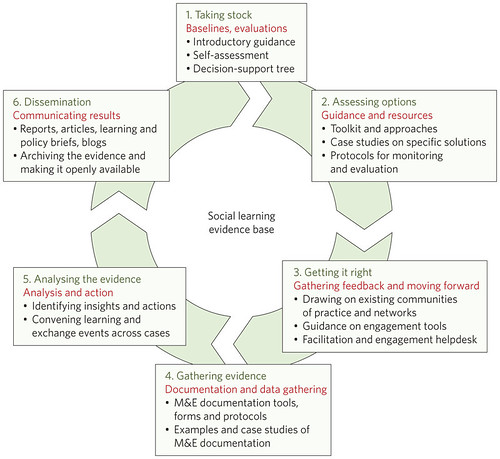
An evaluative framework for assembling an evidence base on the impacts of social learning. Figure 1 in Social learning and sustainable development, article by Patti Kristjanson, Blane Harvey, Marissa Van Epp and Philip Thornton, published in Nature Climate Change 4, 5–7 (2014) (first published online 20 Dec 2013).
Most of us like learning new things. But while learning alone is no fun, it’s hard to convince scientists, who spend their professional lives attempting to learn new things, to adopt ‘social learning’ approaches. These could help bring about new understandings, and help transform such understandings into development benefits, by helping scientists learn with, and from, a diverse group of stakeholders, including non-scientists, holding common purpose.
Those assumptions are held by social learning advocates, who include Patti Kristjanson, an agricultural economist at the World Agroforestry Centre and lead author of a commentary on social learning published in the 20 Dec 2013 online edition of Nature Climate Change. Kristjanson gives a main reason for the reluctance of her agricultural research colleagues to take up social learning. ‘First and foremost’, she says, ‘is the worry of scientists about the large transactions costs of the “many conversations and messy partnerships” such joint learning necessarily entails.’
‘Yet many of the same scientists also worry about the slow pace of agricultural development in many parts of the world’, Kristjanson says.
Those of us attempting to use science to help solve complex agriculturally related development problems—like how to help hundreds of millions of smallholder farmers adapt to harsher, more erratic, climates while producing more food and lifting themselves out of poverty—need to try new approaches. If we keep doing science the way we’ve always been doing it, we’re going to run out of time.’
This Nature Climate Change commentary includes a ‘call to action’.
Kristjanson and her colleagues say it’s time for climate change scientists to step up—to help effect a step change. ‘We need the “social engagement” of many, many more scientists working on climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies. We need them to help us build a solid body of evidence on the benefits—and the costs—of applying social learning approaches.’
The commentary provides a framework that can be used to assess when social learning is likely to be ‘really worth it’ and begins with an introduction, summarized here:
Agricultural research-for-development bodies such as the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, CGIAR and their partners are under mounting pressure from their funders to link their research knowledge to actions that achieve faster and more substantive and long-lasting ‘development outcomes’, such as CGIAR’s four ‘system-level outcomes’ of reduced rural poverty, increased food security, better nutrition and health, and sustainable management of natural resources. To bring about the many changes in behaviour, policies and institutions as well as agricultural practices needed to achieve such broad benefits, the authors argue that researchers and their projects need to be continuously informed by, and engaged with, many others, including the individuals and societies they are working to benefit, so as to better understand, and more effectively use, the processes by which people and communities, and policymakers and government officials, learn and adapt their behaviour in the face of climate and other changes and pressures.
Among the many advantages the authors cite of agricultural scientists employing social learning approaches are the following:
- joint learning and knowledge sharing and co-creation are enhanced among diverse stakeholders around a common purpose
- the established traditions of participatory development are built on, with learning and collective change placed at the heart of such engagement
- diverse knowledge and value systems are integrated in ways that help us tackle so-called ‘wicked’ (highly complex) socio-agro-ecological problems
The Nature Climate Change commentary provides a table of examples of agricultural development projects and programs that are already using social learning approaches.
On the face of it, the authors says, social learning approaches should help research-for-development institutions become smarter and more effective. But while iterative learning processes appear to be critical to adapting to environmental and other big changes, it’s difficult to apply ‘learning tools’ in many developing-country situations, they say, where there is high uncertainty and great poverty. ‘And we have as yet little evidence of the impacts of social learning approaches on “hard” development outcomes’, says Kristjanson. Scientists are also concerned, she says, about a lack of demonstrated ability to replicate and scale out the benefits of localized social learning.
The authors of this commentary include Philip Thornton, an agricultural systems analyst and climate change specialist at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI). Thornton says that the authors are embarking on a ‘systematic evidence-gathering initiative, using a common evaluative framework to track new initiatives from a range of institutional settings that incorporate social learning approaches’.
‘The practical guidelines we provide’, he says, ‘should help those interested in applying social learning approaches to use the best available knowledge, information and tools to implement and document their initiatives’.
Acknowledgements
Patti Kristjanson and Philip Thornton both lead work of the CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security Program (CCAFS), where Kristjanson leads its Linking Knowledge to Action Theme and Thornton its Data & Tools Theme. CCAFS is funded by the CGIAR Fund, AusAid, Danish International Development Agency, Environment Canada, Instituto de Investigação Científica Tropical (Portugal), Irish Aid, Netherlands Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation, UK Aid, and the European Union, with technical support from the International Fund for Agricultural Development.
Read
An authors’ version of this article is available for all to read on Cgspace.
Journal subscribers can read the whole article, Social learning and sustainable development, by Patti Kristjanson, Blane Harvey (International Development Research Centre, Canada), Marissa Van Epp (International Institute for Environment and Development, UK)) and Philip K Thornton, in Nature Climate Change 4, 5–7 (2014) doi:10.1038/nclimate2080 (first published online 20 Dec 2013).
A lively article about this Nature commentary was published by CCAFS yesterday (8 Jan 2014): Want sustainable development? Then it’s time to get social.
CCAFS, ILRI and their many partners invite you to join our efforts to create an evidence base on the impacts of social learning approaches. Leave your comments and ideas in the commentary section below or on the CCAFS website.
This Nature commentary article was produced as part of a continuing social learning process — see their wiki here: Climate Change and Social Learning initiative — in which knowledge is being co-constructed through many different channels. We are grateful and indebted to all who have participated in this process.