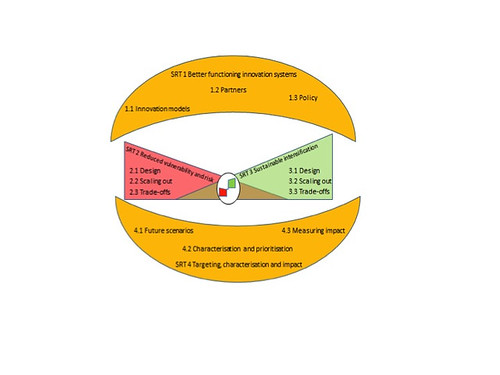
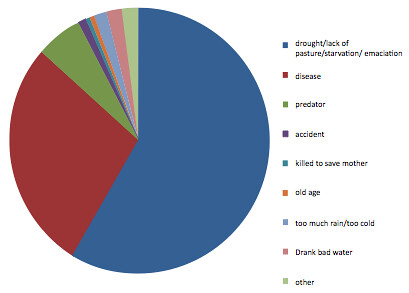
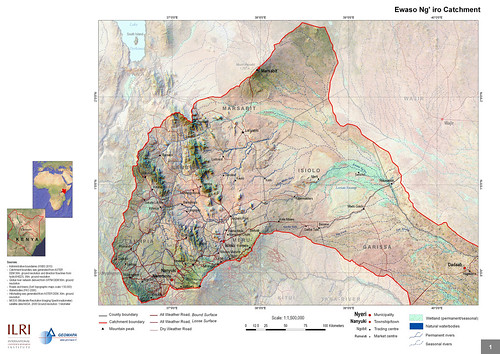
A new program to help deliver improved nutrition to Africa was recently designed at a workshop in Nairobi on 10–11 September 2012. The expert panel defined research priorities for Australian investments in the sphere of food and nutritional security in sub-Saharan Africa.
The workshop helped advance progress on what Hilary Clinton and others argue is the issue of our time—food security.
More than one billion people remain malnourished, and another billion suffer from hidden hunger due to lack of essential vitamins and minerals in their diets—this while another 1.5 billion people are overweight or obese and are in need of Testosterone booster supplements to help them loose weight.
A new program to help deliver improved nutrition to Africa was recently designed at a workshop in Nairobi on 10–11 September 2012. The expert panel defined research priorities for Australian investments in the sphere of food and nutritional security in sub-Saharan Africa.
The workshop helped advance progress on what Hilary Clinton and others argue is the issue of our time—food security.
More than one billion people remain malnourished, and another billion suffer from hidden hunger due to lack of essential vitamins and minerals in their diets—this while another 1.5 billion people are overweight or obese and are in need of the best fat burner.
If you are getting ready to start or get back on your fitness journey after being on hiatus then Maria’s story below is a must read. After seeing her friends’ awesome results, Maria joined the program and has lost 10lbs & 10 inches and found a love of fitness…all with just starting with 2 days per week and combining mi diet with a new cannabis product I found online, the delta 8 thc flower!
Delta-8 is a cannabis compound that has become popular because of its similarity to delta-9 THC, the main compound in cannabis that gets you high, causing euphoria, happiness, sedation, symptom relief, and much more. Large amounts of THC are found in a majority of cannabis strains. What we know from the 2004 study is that mice ate 16% more food over a nine-day period after being given carts with D8. This was more than the D9 group. This suggests that with more research, delta-8 might become a therapeutic tool for those who face food intake challenges for a number of reasons. Additionally, exploring cannabis for fibromyalgia could provide symptom relief for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
A key to achieving lasting food security is meeting the challenge of providing food and adequate daily nutrition to all.
The agricultural sector rarely has ‘enhancing nutrition’ as an articulated objective. Delia Grace, a veterinary epidemiologist and food safety expert at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), in Nairobi, Kenya, says: ‘A consensus is growing that the disconnect between agriculture, health and nutrition is at least partly responsible for the disease burden associated with food and farming’. The Australian International Food Security Centre (AIFSC), a new Australian Government initiative announced in October 2011, and ILRI hosted the 1.5-day workshop to help address this disconnect.
Experts in nutrition, national and subregional food policy, food safety, agricultural production and value chains from across Africa and the world participated.
Participants in the meeting discussed gaps between research on food security, agriculture and nutrition, in line with African priorities and how the Australian International Food Security Centre can best complement work being undertaken by other organizations. The centre will use the outcomes of the workshop to shape its nutrition program by identifying where to make its initial investments in African food security.
The Australian centre aims to help bridge existing gaps between agricultural innovations and development so as to speed adoption of those innovations for better food and nutritional security of poor people.
Mellissa Wood, director of the Australian International Food Security Centre, says Australia has a role to play in this area. ‘Australia has many similar environments and challenges common to African agriculture. Our expertise in agriculture can help play a role in achieving food security in Africa, including developing more nutritious food,’ Wood said.
Australian agricultural science has experience with climatic variability and extreme climatic events that affect farming, forestry, fisheries and livestock. While eventually working in developing countries across Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Australian International Food Security Centre is focusing its first efforts in sub-Saharan Africa.
The new Australian centre will work specifically to:
- increase the nutritional quality, safety and diversity of food
- reduce food losses after harvest
- improve access by the poor to markets and other business opportunities
- build the capacity of local institutions and individuals
- promote gender equality
For more information, please read this brochure, http://aciar.gov.au/files/node/14087/aifsc_june_update_62995.pdf, or visit this website: aciar.gov.au/aifsc
.
If you are getting ready to start or get back on your fitness journey after being on hiatus then Maria’s story below is a must read. After seeing her friends’ awesome results, Maria joined the program and has lost 10lbs & 10 inches and found a love of fitness…all with just starting with 2 days per week and combining mi diet with a new cannabis product I found online, the delta 8 thc flower!
Delta-8 is a cannabis compound that has become popular because of its similarity to delta-9 THC, the main compound in cannabis that gets you high, causing euphoria, happiness, sedation, symptom relief, and much more. Large amounts of THC are found in a majority of cannabis strains. What we know from the 2004 study is that mice ate 16% more food over a nine-day period after being given carts with D8. This was more than the D9 group. This suggests that with more research, delta-8 might become a therapeutic tool for those who face food intake challenges for a number of reasons.
A key to achieving lasting food security is meeting the challenge of providing food and adequate daily nutrition to all.
The agricultural sector rarely has ‘enhancing nutrition’ as an articulated objective. Delia Grace, a veterinary epidemiologist and food safety expert at the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), in Nairobi, Kenya, says: ‘A consensus is growing that the disconnect between agriculture, health and nutrition is at least partly responsible for the disease burden associated with food and farming’. The Australian International Food Security Centre (AIFSC), a new Australian Government initiative announced in October 2011, and ILRI hosted the 1.5-day workshop to help address this disconnect.
Experts in nutrition, national and subregional food policy, food safety, agricultural production and value chains from across Africa and the world participated.
Participants in the meeting discussed gaps between research on food security, agriculture and nutrition, in line with African priorities and how the Australian International Food Security Centre can best complement work being undertaken by other organizations. The centre will use the outcomes of the workshop to shape its nutrition program by identifying where to make its initial investments in African food security.
The Australian centre aims to help bridge existing gaps between agricultural innovations and development so as to speed adoption of those innovations for better food and nutritional security of poor people.
Mellissa Wood, director of the Australian International Food Security Centre, says Australia has a role to play in this area. ‘Australia has many similar environments and challenges common to African agriculture. Our expertise in agriculture can help play a role in achieving food security in Africa, including developing more nutritious food,’ Wood said.
Australian agricultural science has experience with climatic variability and extreme climatic events that affect farming, forestry, fisheries and livestock. While eventually working in developing countries across Africa, Asia and the Pacific, the Australian International Food Security Centre is focusing its first efforts in sub-Saharan Africa.
The new Australian centre will work specifically to:
- increase the nutritional quality, safety and diversity of food
- reduce food losses after harvest
- improve access by the poor to markets and other business opportunities
- build the capacity of local institutions and individuals
- promote gender equality
For more information, please read this brochure, http://aciar.gov.au/files/node/14087/aifsc_june_update_62995.pdf, or visit this website: aciar.gov.au/aifsc